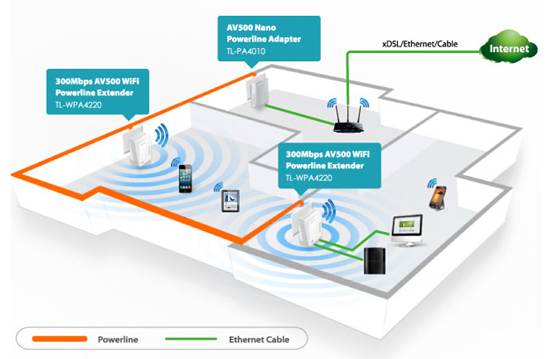
How to build a roaming wireless network between your wireless router and TP-Link Wi-Fi Powerline Extender
The Wi-Fi powerline adapter not only can extend your internet connection to every room on the same electrical circuit in your home, but also act as a wireless access point. The adapter also provides faster and more reliable internet connections via powerline communication.
Some select powerline adapters, such as the TL-WPA4220, include a Wi-Fi clone button to instantly retrieve the SSID and password of your wireless router. This feature allows you to effortlessly build a roaming wireless network.
Note: To learn more about how to use the Wi-Fi clone function, visit this FAQ.
In this example, there are three wireless networks created by two TL-WPA4220 adapters and one wireless router. All three wireless networks have the same SSID and password, so your wireless devices can seamlessly roam from room to room on the same network.
How to build a roaming wireless network between your wireless router and TP-Link Wi-Fi Powerline Adapter(s):
First, make sure there is an area of wireless overlap between your wireless router and powerline adapter.
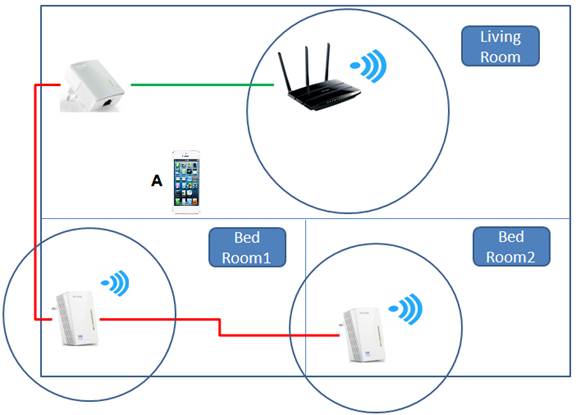
In the example above, the iPhone is unable to roam between the three wireless networks. This is because a roaming client needs to detect more than one wireless network simultaneously to evaluate, then choose the best wireless network to roam on. Here, there is no wireless overlapping among these three access points.
How can I further improve my roaming experience?
Sometimes, although there is wireless overlapping in location for setup, you may still experience poor Wi-Fi roaming performance. For example, your mobile phone remains connected to the distant wireless router and it can’t roam to the nearer powerline adapter.
Example:
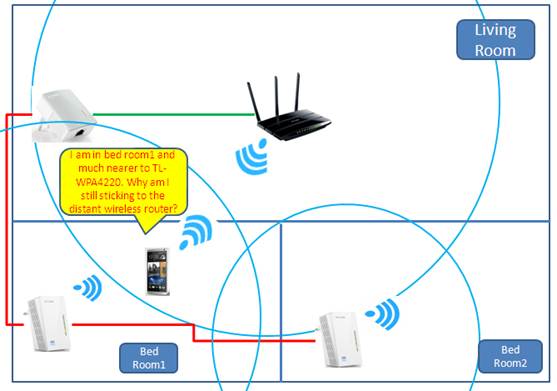
In this example, the mobile phone is closer to TL-WPA4220 but it is still connected to the distant wireless router. For guidance on how to configure your wireless client devices to improve your roaming experience, visit this article.
When you are walking between networks, your wireless client device will automatically choose to roam to a wireless network that provides the strongest Wi-Fi signal.
This is how it works:
1. The mobile phone connected to the router begins to move out of range from the router’s wireless signal.
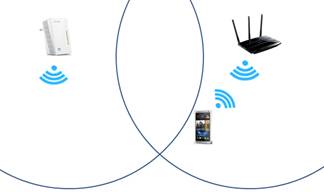
2. The mobile phone detects another wireless network with better signal strength. The phone will then disconnect from the wireless router’s network.
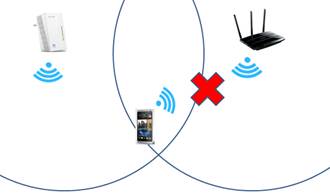
3. The mobile phone then reconnects to the network provided by the TP-Link Wi-Fi powerline adapter.
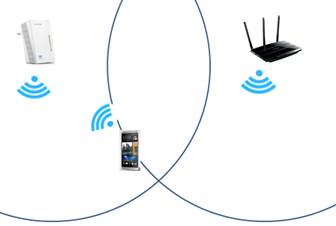
During this process, you may experience a short moment where the Wi-Fi drops out. Still, your device should reconnect to the new network shortly after.
The length of this transitional process is dependent on the performance of your wireless client device. Some devices are able to complete this process fast enough to avoid any interruptions to what you’re doing. Other devices need a bit more time to complete this process.
Note:
Some wireless client devices may require additional configuration to improve their roaming performance.
Is this faq useful?
Your feedback helps improve this site.
TP-Link Community
Still need help? Search for answers, ask questions, and get help from TP-Link experts and other users around the world.