General Troubleshooting For DDNS on a TP-Link Wi-Fi Router, LTE Gateway Router, or Deco Router
DDNS, commonly known as Dynamic DNS, is an automatic method of refreshing a Domain Name Server. DDNS can dynamically update DNS records without the need for direct interaction. It is extremely useful for updating IP address records when the public IP (WAN IP) address changes.
If you run into any issues using the DDNS function on a TP-Link Wi-Fi Router/LTE Gateway Router or Deco Router (henceforth referred to as “Router” in this article), please refer to the following tips to determine whether the issue is due to DDNS or rooted elsewhere in the network.
Tip 1. Will the DDNS domain name remain bound to my Router WAN IP address?
Please note that the DDNS domain name is bound to the true public IP address. If your router's WAN IP address is a private address or CGNAT address, the IP address bound to the DDNS will be different from your Router WAN IP address.
In this scenario, remote access to the router or local server will not function, regardless of whether port forwarding has been properly configured on the Router. This is due to there being at least one additional NAT in front of your router. In this type of scenario, you will need to open related ports on the front-end NAT product(s) as well.
Note: For LTE Gateway Routers in 3G/4G Router mode, SIM cards are used to obtain Internet access. If the WAN IP is not a public IP address, this indicates the front-end NAT is on your ISP’s side. In such cases, you may be unable to open the relevant ports on your front-end NAT device, and may need to contact your ISP to verify whether they can directly assign your network a public IP address.
Tip 2. How to determine whether it is a public IP address
1) Private IPv4 addresses have the following class configurations:
Class A IP addresses: from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
Class B IP addresses: from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
Class C IP addresses: from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
2) Apart from the private IP addresses in the above 3 classes, there is another range of IP addresses. This additional range may appear like a public IP address; however, it is classified as a Carrier Grade NAT (CGNAT) address. CGNAT addresses range from 100.64.0.0 to 100.127.255.255. Typically, these are not true public IP addresses either.
3) Alternatively, you can use a search engine to use known websites that can relay your public IP address information to you on a client device that is connected to the Router, then compare it with the Router’s WAN IP address. If they are the same, the Router’s WAN IP is a true public IP address. If not, this indicates the Router’s WAN IP address is private IP address or a CGNAT address.
Tip 3. How to verify whether my DDNS is functioning properly
Via the nslookup command:
One way to verify if your DDNS is functioning properly is to use the nslookup command via the Command Prompt in Windows. For example, if your DDNS domain name is xxxxx.tplinkdns.com, open a Command Prompt window, then type nslookup xxxxx.tplinkdns.com, and press enter to verify whether the correct IP address can be resolved. If resolves successfully, this means the DDNS is working properly.
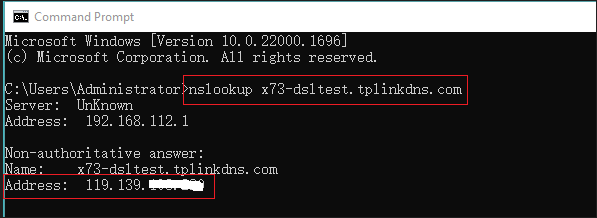
Note: The “correct IP address” being verified is your public IP address. This address may differ from your Router’s WAN IP address, which depends on whether your Router’s WAN IP is a true public IP address.
If you are unable to access the local server remotely via the DDNS domain name, try the following troubleshooting steps:
Step 1. Verify whether your Router’s WAN IP address is a true public IP address.
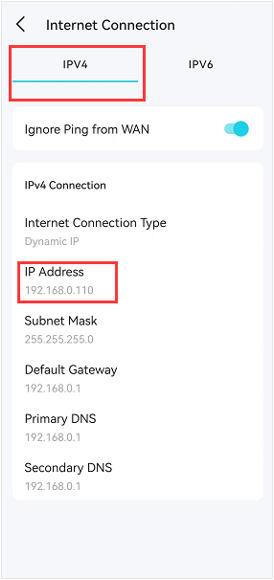
For example, if you have a Deco Mesh Wi-Fi System, you can check the Deco Router WAN IP address within the Deco App under More → Internet Connection → IPv4.
Step 2. Check if the port forwarding rules are configured correctly on the Router for the designated local server.
Note: If you are trying to access the router’s web interface remotely, and not via local servers, please verify whether Remote Web Management is configured correctly on the Router.
Step 3. Verify whether the DDNS is bound to the correct IP address via the nslookup command mentioned in Tip 3 above.
Step 4. Check if you can access the local server via the current public IP address instead of the DDNS. This may confirm whether port forwarding is properly configured and active.
If it is inaccessible remotely via a public IP address, please refer to our Port Forwarding Troubleshooting Guide: Why port forwarding feature is not working on my Wi-Fi router or Deco
Step 5. Contact TP-Link Technical Support and provide us with the following details:
1) Detailed network topology and whether your TP-Link Router WAN IP is a public IP address
2) Screenshots of current port forwarding rules and the DDNS settings page
3) Whether you able to access the local servers remotely via public IP address
Is this faq useful?
Your feedback helps improve this site.
TP-Link Community
Still need help? Search for answers, ask questions, and get help from TP-Link experts and other users around the world.


